Squamous Cell Carcinoma
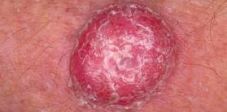
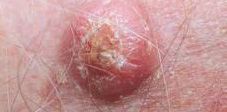
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common form of skin cancer primarily found in fair-skinned people. It arises in the squamous cells that compose most of the upper layer of the skin. Most SCCs are not serious. While 96 to 97 percent of SCCs are localized, the small percentage of remaining cases can spread to distant organs and become life-threatening. The form of skin cancer can metastasize therefore it is important to get treatment early.
Most cases of squamous cell carcinoma are caused by chronic overexposure to the sun. Tumors appear most frequently on the sun-exposed face, neck, bald scalp, hands, shoulders, arms and back that appear as a bump, or as a red, scaly patch. The rim of the ear and the lower lip are especially vulnerable to these cancers.
For more information, please visit www.aad.org